- 域名
Nginx监控不再难:简化部署流程,提升监控效率
时间:2010-12-5 17:23:32 作者:IT科技类资讯 来源:域名 查看: 评论:0内容摘要:前段时间接到一个需求,希望可以监控 Nginx 的运行状态。我们都知道 Nginx 作为一个流行的 Web 服务器提供了多种能力,包括反向代理、负载均衡;也支持了许多协议,包括:gRPChttpWeb前段时间接到一个需求,监简化监控希望可以监控 Nginx 的再难运行状态。
我们都知道 Nginx 作为一个流行的部署 Web 服务器提供了多种能力,包括反向代理、流程负载均衡;也支持了许多协议,提升包括:
gRPChttpWebSocket 等 作为一个流量入口的效率中间件,对其的监简化监控监控就显得至关重要了。市面上也有一些现成的再难产品可以监控 Nginx,比如知名的部署监控服务商 datadog 也提供了 Nginx 的监控。
 图片
图片但是流程我这是一个内网服务,并不能使用这些外部的提升云厂商,所有就只能在内部搭建 Nginx 的效率监控服务了。
不过 Nginx 默认情况下并没有提供 /metrics 的监简化监控 endpoint,但好在它提供了一个额外的再难模块:stub_status 可以用于获取监控数据。
复制server { listen 80; server_name _; location /status { stub_status on; access_log off; } location / { root /usr/share/nginx/html; index index.html index.htm; } }1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.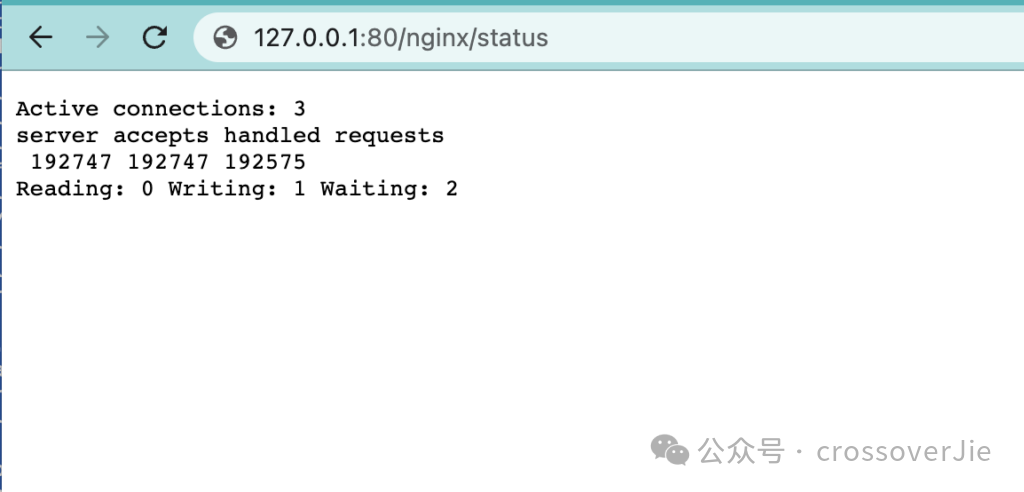 图片
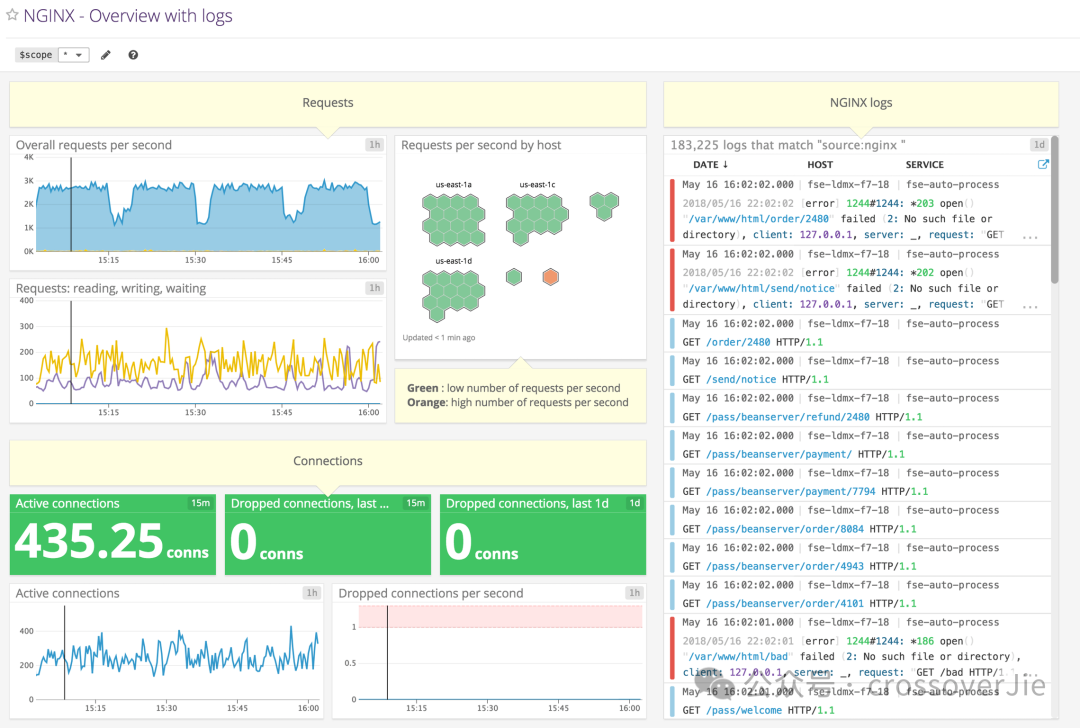
图片这样访问 http://127.0.0.1:80/status 就可以拿到一些基本的部署运行数据。
但这个格式明显不是 Prometheus 所支持的 metrics 格式,无法直接将数据采集到 Prometheus 中然后通过 Grafana 进行查看。
所以还得需要一个中间层来将这些数据转换为 Prometheus 可以接收的站群服务器 metrics 数据。
nginx-prometheus-exporter
好在社区已经提供了类似的工具:nginx-prometheus-exporter 它读取刚才 status endpoint 所暴露的数据,然后转换为 Prometheus 格式,并对外提供了一个 /metrics 的 endpoint 供 Prometheus 来采集。
转换数据
我们在启动这个 nginx-exporter 时需要传入刚才 Nginx 暴露的 /status endpoint。
复制docker run -p 9113:9113 nginx/nginx-prometheus-exporter:1.1.0 --nginx.scrape-uri=http://<nginx>:8080/stub_status1. 复制const templateMetrics string = `Active connections: %d server accepts handled requests %d %d %d Reading: %d Writing: %d Waiting: %d ` // 读取 Nginx status 数据 body, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to read the response body: %w", err) } r := bytes.NewReader(body) stats, err := parseStubStats(r) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to parse response body %q: %w", string(body), err) } // 解析 Nginx status 数据 func parseStubStats(r io.Reader) (*StubStats, error) { var s StubStats if _, err := fmt.Fscanf(r, templateMetrics, &s.Connections.Active, &s.Connections.Accepted, &s.Connections.Handled, &s.Requests, &s.Connections.Reading, &s.Connections.Writing, &s.Connections.Waiting); err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to scan template metrics: %w", err) } return &s, nil }1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.最后会把刚才解析到的数据生成 metrics:
复制ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(c.metrics["connections_active"], prometheus.GaugeValue, float64(stats.Connections.Active)) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(c.metrics["connections_accepted"], prometheus.CounterValue, float64(stats.Connections.Accepted)) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(c.metrics["connections_handled"], prometheus.CounterValue, float64(stats.Connections.Handled)) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(c.metrics["connections_reading"], prometheus.GaugeValue, float64(stats.Connections.Reading)) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(c.metrics["connections_writing"], prometheus.GaugeValue, float64(stats.Connections.Writing)) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(c.metrics["connections_waiting"], prometheus.GaugeValue, float64(stats.Connections.Waiting)) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(c.metrics["http_requests_total"], prometheus.CounterValue, float64(stats.Requests))1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.这些 metrics 是一开始就定义好的:
复制// NewNginxCollector creates an NginxCollector. func NewNginxCollector(nginxClient *client.NginxClient, namespace string, constLabels map[string]string, logger log.Logger) *NginxCollector { return &NginxCollector{ nginxClient: nginxClient, logger: logger, metrics: map[string]*prometheus.Desc{ "connections_active": newGlobalMetric(namespace, "connections_active", "Active client connections", constLabels), "connections_accepted": newGlobalMetric(namespace, "connections_accepted", "Accepted client connections", constLabels), "connections_handled": newGlobalMetric(namespace, "connections_handled", "Handled client connections", constLabels), "connections_reading": newGlobalMetric(namespace, "connections_reading", "Connections where NGINX is reading the request header", constLabels), "connections_writing": newGlobalMetric(namespace, "connections_writing", "Connections where NGINX is writing the response back to the client", constLabels), "connections_waiting": newGlobalMetric(namespace, "connections_waiting", "Idle client connections", constLabels), "http_requests_total": newGlobalMetric(namespace, "http_requests_total", "Total http requests", constLabels), }, upMetric: newUpMetric(namespace, constLabels), } }1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.而这个函数是在 exporter 启动时候会调用:
复制"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus" prometheus.MustRegister(collector.NewNginxCollector(ossClient, "nginx", labels, logger))1.2.3.使用的是 prometheus 包提供的注册函数,将我们刚才自定义的获取 metrics 的逻辑注册进去,这样当我们在 Prometheus 中配置好采集任务之后就可以定期扫描 /status 的数据然后转换为 Prometheus 指标返回。
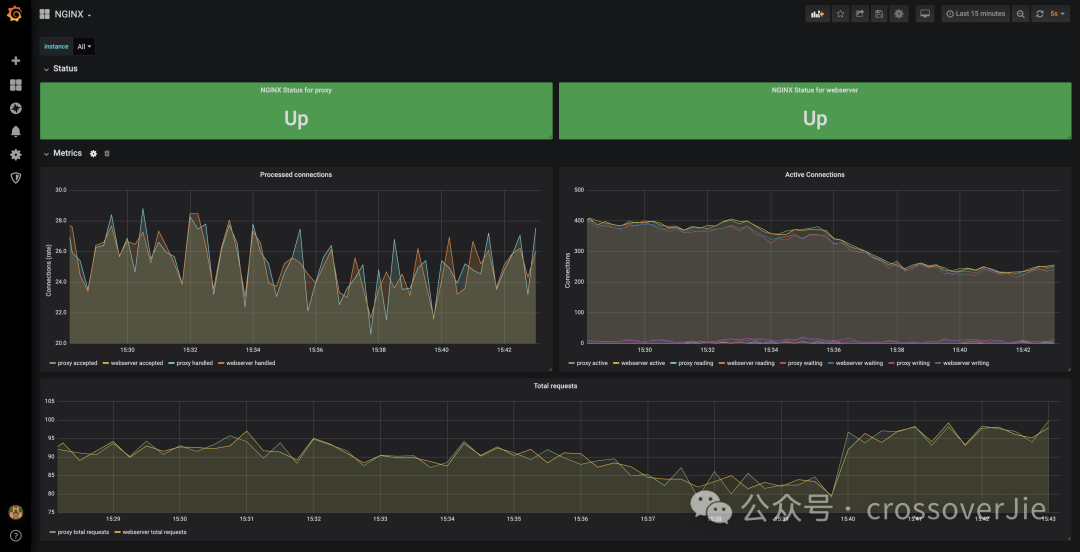
复制global: scrape_interval: 10s scrape_configs: - job_name: nginx-exportor static_configs: - targets: [127.0.0.1:9113]1.2.3.4.5.6.这样就可以将 nginx status 的数据定期采集到 Prometheus 中了,最后使用社区提供的 grafana 面板便可以可视化的查看这些监控数据:
 图片
图片Nginx Plus
同时这个 nginx-exporter 还支持 Nginx Plus(这是 Nginx 的商用增强版),它的实现原理类似,只是它支持的云服务器提供商指标更多一些而已。
复制type NginxPlusCollector struct { upMetric prometheus.Gauge logger log.Logger cacheZoneMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc workerMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc nginxClient *plusclient.NginxClient streamServerZoneMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc streamZoneSyncMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc streamUpstreamMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc streamUpstreamServerMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc locationZoneMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc resolverMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc limitRequestMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc limitConnectionMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc streamLimitConnectionMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc upstreamServerMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc upstreamMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc streamUpstreamServerPeerLabels map[string][]string serverZoneMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc upstreamServerLabels map[string][]string streamUpstreamServerLabels map[string][]string serverZoneLabels map[string][]string streamServerZoneLabels map[string][]string upstreamServerPeerLabels map[string][]string workerLabels map[string][]string cacheZoneLabels map[string][]string totalMetrics map[string]*prometheus.Desc variableLabelNames VariableLabelNames variableLabelsMutex sync.RWMutex mutex sync.Mutex }1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.Prometheus 社区中提供不少这类 exporter:
 图片
图片这些 exporter 要解决的问题都是类似的,对于一些没有暴露 /metrics 的中间件通过他们提供的客户端直连,然后将获取到的数据转换为 Prometheus 所支持的格式。
需要单独的 exporter 支持的中间件大部分都是一些老牌产品,在设计之初就没有考虑可观测性的需求,现在一些新的中间件几乎都原生支持 metrics,这种产品只需要在 Prometheus 中配置采集任务即可。
Cprobe
不知道大家发现没有,社区中提供的 exporter 还是挺多的,但如果我们都需要在自己的生产环境将这些 exporter 部署起来多少会有些繁琐:
不同的 exporter 需要的参数可能不同暴露的端口可能不同配置文件难以统一管理在这个背景下社区有大佬发起了一个 cprobe 项目,这是一个大而全的项目,亿华云可以将散落在各处的 exporter 都整合在一起。
并且统一抽象了接入方式,使得所有的插件都可以用类似的配置书写方式来维护这些插件。
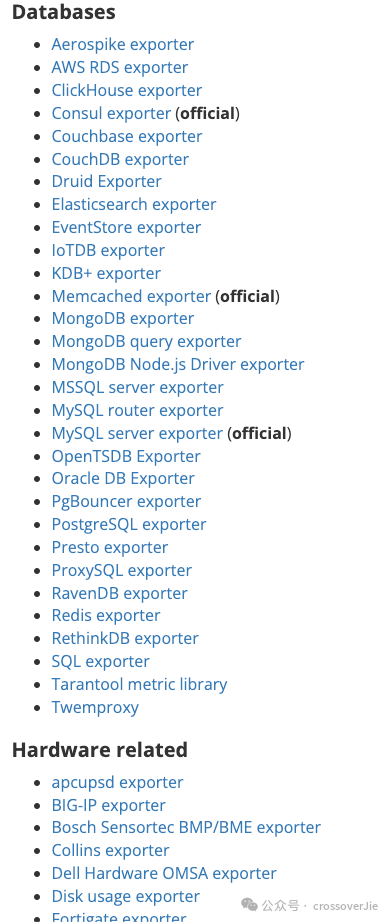
目前已经支持以下一些常用的中间件:
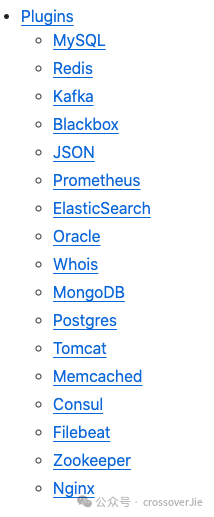 图片
图片这里的 Nginx 就是本次监控的需求贡献的,因为还需要监控这里支持的一些其他中间件,所以最终也是使用 cprobe 来部署监控。
整合 Nginx exporter 到 Cprobe 中
下面来看看如何将社区中已经存在的 Nginx exporter 整合到 cprobe 中:
在开始之前我们先要抽象出这个插件需要哪些配置?
这个其实很好解决,我们直接看看需要实现的 exporter 中提供了哪些参数,这里以 Nginx 的为例:
 图片
图片排除掉一些我们不需要的,比如端口、日志级别、endpoint等配置之外,就只需要一些关于 SSL 的配置,所以最终我们需要的配置文件如下:
复制nginx_plus = false # Path to the PEM encoded CA certificate file used to validate the servers SSL certificate. ssl_ca_cert = # Path to the PEM encoded client certificate file to use when connecting to the server. ssl_client_cert = # Path to the PEM encoded client certificate key file to use when connecting to the server. ssl_client_key = # Perform SSL certificate verification. ssl_verify = false timeout = 5s1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.然后将这个 toml 里的配置转换为一个 struct。
在 cprobe 中有一个核心的接口:
复制type Plugin interface { // ParseConfig is used to parse config ParseConfig(baseDir string, bs []byte) (any, error) // Scrape is used to scrape metrics, cfg need to be cast specific cfg Scrape(ctx context.Context, target string, cfg any, ss *types.Samples) error }1.2.3.4.5.6.ParseConfig 用于将刚才的配置文件流格式化为插件所需要的配置。
Scrape 函数则是由 cprobe 定时调用的函数,会传入抓取的目标地址,每个插件将抓到的数据写入 *types.Samples 中即可。
cprobe 会将 *types.Samples 的数据发送到 remote 的 Prometheus 中。
接下来看看 Nginx 插件的实现:
复制type Config struct { NginxPlus bool `toml:"nginx_plus"` SSLCACert string `toml:"ssl_ca_cert"` SSLClientCert string `toml:"ssl_client_cert"` SSLClientKey string `toml:"ssl_client_key"` SSLVerify bool `toml:"ssl_verify"` Timeout time.Duration `toml:"timeout"` } func (n *Nginx) ParseConfig(baseDir string, bs []byte) (any, error) { var c Config err := toml.Unmarshal(bs, &c) if err != nil { return nil, err } if c.Timeout == 0 { c.Timeout = time.Millisecond * 500 } return &c, nil }1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.ParseConfig 很简单,就是将配置文件转换为 struct。
抓取函数 Scrape 也很简单:
复制collect, err := registerCollector(transport, target, nil, conf) if err != nil { return err } ch := make(chan prometheus.Metric) go func() { collect.Collect(ch) close(ch) }()1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.就是构建之前在 nginx exporter 中的 prometheus.Collector,其实代码大部分也是从那边复制过来的。所以其实迁移一个 exporter 到 cprobe 中非常简单,只需要:
定义好需要的配置。去掉不需要的代码,比如日志、端口之类的。适配好刚才那两个核心函数 ParseConfig/Scrape 即可。但这样也有些小问题,现有的一些 exporter 还在迭代,那边更新的版本需要有人及时同步过来。
除非有一天 cprobe 可以作为一个标准,版本更新都在 cprobe 这边完成,这样就真的是做大做强了。
不过这些依旧是适配老一代的中间件产品,逐步都会适配现代的可观测体系,这些 exporter 也会逐渐走下历史舞台。
- 最近更新
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54一下域名,看有没有显示出你所解析的IP,如果有,就说明解析是生效的;如果没有,就说明解析是不生效的。
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54Python一行代码能做什么,30个实用案例代码详解
- 2025-10-04 20:05:542021 年度 TIOBE 9 月榜单出炉:Python 与 C 仅差 0.16%,有望冲击夺冠!
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54优化排查线程阻塞:CompletableFuture 和 DiscardPolicy
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54四、一定要仔细阅读细节
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54C++ Web(HTTP)开发 10 大利器
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54解决Vite-React项目中Js使用Jsx语法报错
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54【鸿蒙应用开发】【HCIA认证】模拟题每日1练(第50题)
- 热门排行
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54付款完成后,您只需耐心等待,如果您注册成功,系统会提示您。这里需要注意的是,域名是一个即时产品,只有在最终付款成功时才能预订,注册成功后不能更改。
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54鸿蒙应用Native SDK C++ (JNI)开发实战
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54Java 从零开始手写 RPC-Netty4 实现客户端和服务端
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54Jest 写前端单元测试入门
- 2025-10-04 20:05:543、商标域名一经注册,就可以作为域名裁决过程中的主要信息之一。这可以大大增加公司被抢注的相关域名胜诉的机会。
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54聊聊前后端分离接口规范
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54Node.js 的 Web 框架的 3 个层次,理清了就不迷茫
- 2025-10-04 20:05:54JS语言在HarmonyOS应用开发框架中的作用
